Table of Contents
- Introduction
- 1. 2025 in Review: Macroeconomic Backdrop
- 2. 2025 in Review: Technology Sector
- 3. 2025 in Review: Frontier AI Labs
- 4. 2025 in Review: Open-Source and Open-Weight Models
- 5. 2025 in Review: Government Adoption
- 6. 2025 in Review: Regulatory Developments
- A Year to Remember
Introduction
The pace of value creation in AI compressed timelines that once spanned years into quarters. Products launched in early 2025, from deep research capabilities to memory features to agentic coding tools, are already table stakes. Valuations recalibrated sharply, with leading frontier labs reaching $300–500 billion and hyperscaler AI capex exceeding $350 billion in aggregate. Government procurement moved from pilots to workforce-scale deployment. China’s open-weight ecosystem emerged as a credible alternative to Western closed models. This review synthesizes the key developments across macro, technology, frontier labs, open-source, government adoption, and regulation, providing a structured lens on a year that reshaped the competitive landscape before most participants could fully internalize the prior quarter.
I. 2025 in Review: Macroeconomic Backdrop
1.1 Markets and Monetary Policy
- Monetary policy set the tone for the year. Inflation proved persistent, opening at 3.0% in January and easing only marginally to 2.9% by year-end, remaining stubbornly above the Federal Reserve’s 2% target.

- The labor market, meanwhile, showed clear signs of softening. Unemployment rose from 4% in January to 4.4% by September, according to data released in November following delays from the government shutdown.

- Payroll growth followed a similar trajectory, slowing from 143,000 jobs in January to 119,000 in September.

Source: (Harvard Gazette)
- Sticky inflation and a weakening labor market raised stagflation concerns, placing the Fed’s dual mandate in direct tension. Policymakers faced a difficult balancing act and held rates steady through the first half of the year, despite persistent pressure from the Trump administration to ease and the President’s repeated criticism of Chair Powell as “Mr. Too Late.” The Fed held rates steady through the first half of the year despite persistent pressure from the Trump administration to ease. When policymakers did act, they moved decisively, delivering three consecutive rate cuts totaling 75 basis points across September, October, and December. The most recent reduction on December 10 came with a divided 9-3 vote, underscoring internal debate over the path forward.
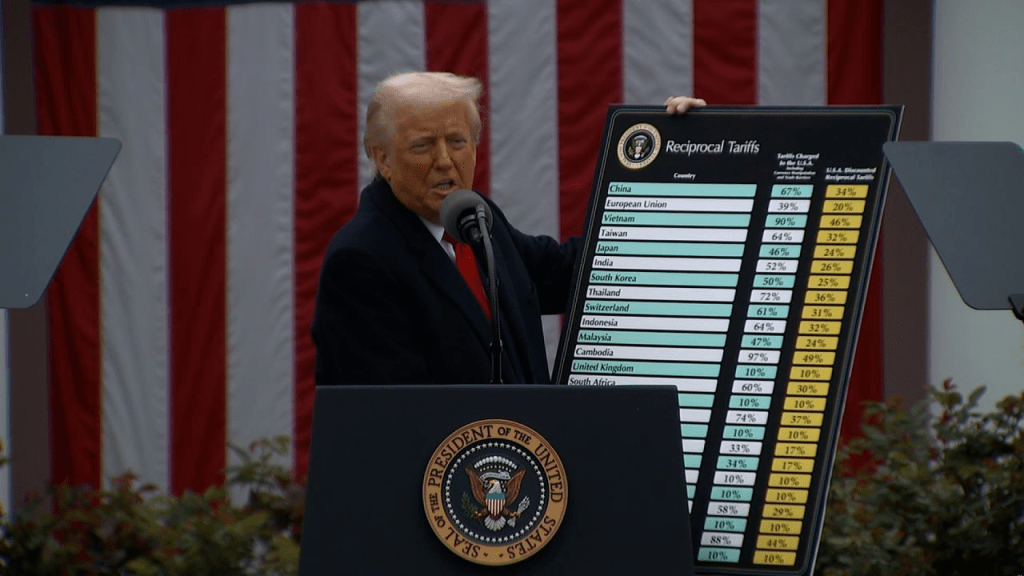
- Trade and fiscal policy introduced additional volatility. On April 2, dubbed “Liberation Day,” the administration unveiled a 10% baseline tariff on most imports, alongside elevated reciprocal rates targeting countries with significant bilateral trade surpluses. Markets sold off sharply: the S&P 500 dropped 4.8% and the Nasdaq fell 6% the following session, wiping out $3.1 trillion in market value in the steepest single-day decline since 2020.

Source (Center for American Progress)
- The Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), led by Elon Musk, aimed to reduce federal spending but saw its efforts largely offset by the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act,” which added over $4 trillion to projected deficits. Musk departed in May, and DOGE was disbanded by November.
1.2 Asset Class Performance
- Asset class performance reflected the uncertain environment. Gold led the way, surpassing $4,000 per ounce for the first time on October 10 and closing the year up 63%.
- Digital assets rallied early on regulatory optimism. On January 17, the $TRUMP meme coin launched on the Solana platform and surpassed a $10 billion market cap within an hour. In March, the administration established a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve, and by October 6, Bitcoin reached a record $124,000. However, risk-off sentiment took hold on October 10, triggering a $19 billion single-day liquidation that sparked a sharp reversal. The selloff wiped $1.2 trillion from the market. The selloff wiped $1.2 trillion from the market. Later in October, on October 23, President Trump pardoned Binance founder Changpeng “CZ” Zhao, reversing his 2024 conviction related to anti-money-laundering compliance and reinforcing a more permissive regulatory environment for digital assets. By year-end, Bitcoin was down 9% YTD.
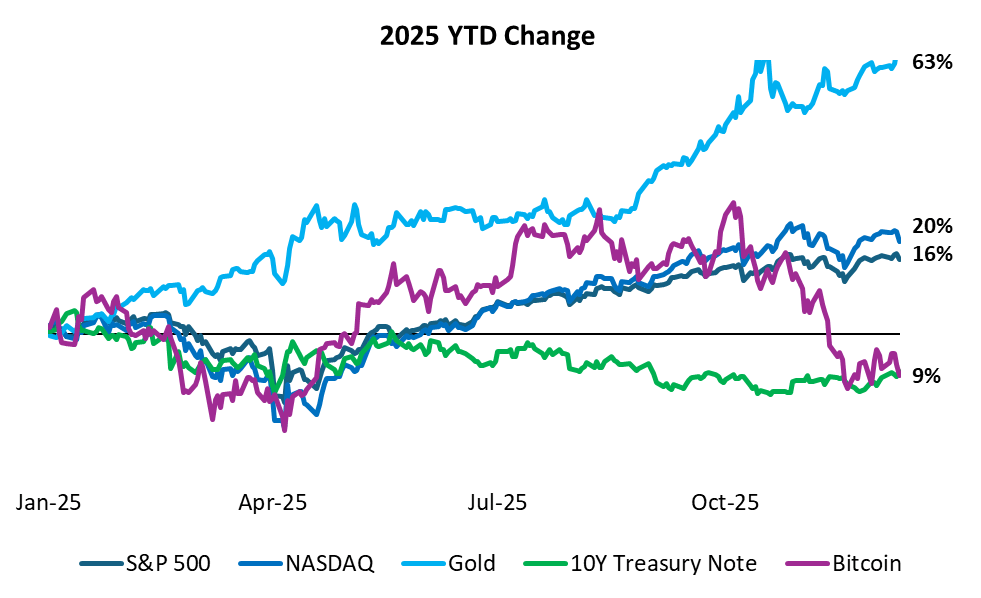
- As of December 12th, equities rebounded from the April Liberation Day selloff, with the Nasdaq gaining 20% and the S&P 500 rising 16%, while the 10-year Treasury yield fell 38 basis points.
- The U.S. dollar weakened sharply, posting its steepest annual decline in three decades. The dollar index fell to 98.6 following the December rate cut, its lowest level since late October, capping a year in which it dropped over 10% through the first half alone—the largest such decline since 1973. The greenback fell against major currencies, including the euro and sterling, as expectations for continued rate cuts into 2026 prompted broad selling pressure.
II. 2025 in Review: Technology Sector
II. 2025 in Review: Technology Sector
On February 3, 2025, President Trump signed Executive Order 14196 directing the Treasury and Commerce Departments to establish a U.S. sovereign investment vehicle within twelve months. The strategy relied on transaction-based investments rather than surplus funding. On August 22, the administration converted $8.9 billion of CHIPS Act grants into an approximately 9.9% equity stake in Intel. The government also obtained special governance rights in the Nippon Steel–U.S. Steel transaction. These actions aligned the federal capital directly with semiconductor manufacturing and industrial assets designated as strategically important.

(Source: Truth Social)
In January 2025, President Trump announced the $500 billion Stargate Project, backed by OpenAI, SoftBank, Oracle, and Abu Dhabi’s MGX, with $100 billion allocated for initial deployment across five U.S. data-center campuses totaling approximately 10 gigawatts of capacity.

(Source: BBC News)
- On March 3, TSMC announced a $100 billion expansion of its U.S. operations, bringing total U.S. commitments to $165 billion across advanced fabs, packaging facilities, and an R&D center in Arizona.
- Nvidia announced plans in April to produce up to $500 billion of AI infrastructure domestically over four years, including Blackwell chip production at TSMC’s Phoenix facility and U.S. supercomputer manufacturing with Foxconn and Wistron.
- After a temporary January service suspension and multiple enforcement extensions through executive orders, TikTok’s U.S. operations were transferred on September 22 to a majority-American ownership group led by Oracle, which assumed oversight of the U.S. recommendation algorithm.
- For rare earth, the U.S. Department of War issued a $150M loan to MP Materials to boost domestic rare earth processing, countering China’s influence and securing critical mineral supply under the July 2025 One Big Beautiful Bill.
- In parallel, the administration signaled a sovereign-adjacent industrial strategy around critical minerals, highlighted by a $1.4B rare-earth magnet partnership involving Vulcan Elements and ReElement, including $700M in conditional loans (DoD/OSC) and a $50M Commerce equity stake (plus warrants), targeting up to 10,000 metric tons of NdFeB magnet material

(Source: Vulcan Elements)
2.2 Selected Technology Transactions
In 2025, the U.S. tech and AI landscape was defined by a rapid escalation in strategic capital formation—spanning sovereign-adjacent infrastructure announcements, semiconductor re-shoring commitments, and major platform transactions—alongside a parallel set of policy and commercialization catalysts that shaped labor mobility, autonomy deployment, and the monetization path for the AI supply chain. The common thread was convergence: chips, data centers, networking, and regulatory posture increasingly moved in lockstep with frontier AI deployment.
Key developments:
- January 2025: President Trump announced the $500B Stargate Project, backed by OpenAI, SoftBank, Oracle, and MGX, with $100B allocated for initial deployment across five U.S. data-center campuses (~10GW).
- March 3, 2025: TSMC announced a $100B expansion of U.S. operations, bringing total U.S. commitments to $165B across advanced fabs, packaging, and an Arizona R&D center
- March 18, 2025: Google Cloud acquires Wiz in a landmark cybersecurity deal valued at $32 billion, integrating Wiz’s cloud security platform to strengthen multicloud defenses and AI‑era protections. Wiz was previously valued at about $12 billion in its last funding round
- April 2025: Nvidia announced plans to produce up to $500B of AI infrastructure domestically over four years, including Blackwell production at TSMC Phoenix and U.S. supercomputer manufacturing with Foxconn and Wistron
- June 2025: Tesla launched an invite-only robotaxi pilot in Austin
- July 2025: HPE closed its ~$14B acquisition of Juniper Networks, consolidating an AI-native networking stack
- July 2025: Figma completed its IPO at $33/share, raising ~$1.2B (implied ~$19.3B fully diluted valuation at pricing)
- September 22, 2025: After a temporary January suspension and multiple enforcement extensions, TikTok’s U.S. operations were transferred to a majority-American ownership group led by Oracle, which assumed oversight of the U.S. recommendation algorithm
- September 2025: The White House advanced a proposed $100K H-1B fee, rattling tech and other H-1B-reliant sectors.
- September 2025: Electronic Arts agreed to a $55B take-private backed by Saudi PIF (plus Silver Lake and Affinity Partners)
- October 2025: Nvidia became the first $5T public company; separately, Nvidia announced a $1B investment in Nokia tied to AI-RAN and 6G initiatives
- November 2025: Waymo expanded its freeway roadmap and outlined a path toward material scale (including broader metro coverage and new-city expansion planning)
- November 2025: Tesla shareholders approved Elon Musk’s 1 trillion performance-based compensation package, with ~75% support
- December 2025: IBM agreed to acquire Confluent for $11B, positioning streaming data infrastructure as a core enterprise AI layer
- December 2025: President Trump to allow Nvidia H200 exports to China (under a U.S. government 25% revenue-sharing condition), marking a notable late-year policy pivot
2.3 Energy and Power for AI
- On November 18, 2025, the Department of Energy finalized a $1 billion loan to Constellation Energy to restart the Crane Clean Energy Center (formerly Three Mile Island Unit 1), an 835-megawatt nuclear facility shut down in 2019 and scheduled to restart by 2027.
- Microsoft had previously signed a 20-year power purchase agreement with Constellation tied to U.S. data-center demand.
- In June, Meta signed a separate 20-year agreement with Constellation for the full 1,121-megawatt output of the Clinton Clean Energy Center in Illinois.
- Google entered a multibillion-dollar agreement with Commonwealth Fusion Systems for 200 megawatts of fusion power expected in the 2030s.
2.4 Hyperscaler Capital Deployment

- Microsoft entered 2025 guiding to approximately $80 billion of capital spending (YouTube interview), and by August 1st, its Capex was $64.5 billion according to its latest 10K, supplemented by a $9.7 billion agreement with IREN to secure Nvidia chip capacity.
- Alphabet began the year targeting roughly $75 billion of capex and raised its 2025 outlook to approximately $91–93 billion by Q3 as AI-driven cloud and data-center demand increased.
- Amazon guided to capital spending near $100 billion early in the year and increased to $125 billion as reported Q3 2025, with investment increasingly concentrated in AWS data centers and custom AI silicon, while separately pledging $50 billion to expand U.S. government AI infrastructure beginning in 2026 and cutting more than 1,800 roles across gaming, AI search, and advertising.
- Meta initially guided to capital spending in the mid-$60 billion range in January 2025 and later in Q3 2025 its 2025 outlook was adjusted to approximately $70–72 billion, while committing up to $600 billion toward U.S. infrastructure and jobs focused on AI data centers, including a $27 billion facility in Louisiana, a $1.5 billion site in Texas, a $1 billion investment in Wisconsin, and a $27 billion joint venture with Blue Owl Capital for the Hyperion AI data center.
- Apple announced its $500 billion U.S. investment commitment over four years, including AI-related infrastructure. A Harvard economist estimated that 92% of U.S. GDP growth in the first half of 2025 was attributable to AI data-center and technology investment.
- Amid reshoring pressure, Trump threatened a 25% tariff on iPhones not made in the U.S.; Apple responded with its Feb. 24 pledge to spend $500B domestically over four years, add ~20,000 jobs, and double its Advanced Manufacturing Fund to $10B—while not committing to U.S.-based iPhone production.
2.5 Neocloud Infrastructure Buildout
AI infrastructure became a primary arena for scale advantages in 2025, with neoclouds using IPO proceeds, long-dated capacity leases, and vertical integration attempts to lock in power, land, and GPUs. The year’s highest-signal moves centered on CoreWeave’s public-market financing and contract stack, the durability of hyperscale demand signals, and the emergence of alternative capacity providers (including Nebius) as capital formation accelerated across the GPU supply chain.
CoreWeave and adjacent infrastructure:
- March 2025: CoreWeave priced its IPO at $40/share, raising $1.5B at ~$19B valuation (testing public appetite for capital-intensive AI infrastructure).
- June 2025: CoreWeave signed two 15-year leases with Applied Digital to deliver 250MW at Ellendale, ND, with ~$7B of projected revenue over the term and expansion optionality.
- July 2025: CoreWeave announced a ~$9B all-stock plan to acquire Core Scientific (targeting ~1.3GW of capacity); the deal terminated on October 30, 2025 after the required shareholder vote failed.
- September 2025: Nebius signed a $17.4B, five-year AI infrastructure agreement with Microsoft; shares jumped ~47% on announcement (a visible public-market repricing of non-hyperscaler GPU capacity).
- November 2025: Vast Data signed a $1.17B deal with CoreWeave tied to AI cloud infrastructure delivery.
III. 2025 in Review: Frontier AI Labs
3.1 OpenAI
M&A and Vertical Integration
In 2025, OpenAI accelerated vertical integration across hardware, product infrastructure, and enterprise software, using acquisitions and minority investments to internalize critical capabilities and extend its platform beyond models into devices and applications.
Key transactions:
- io acquisition (June 2025): Acquired for $6.5B (all-stock). Brought a 55-person, ex-Apple hardware team in-house; LoveFrom assumed creative leadership. Sam Altman and Jony Ive unveiled a screen-free, smartphone-sized prototype in November, emphasizing simplicity and playfulness, with launch expected within two years. OpenAI disclosed plans to ship 100M AI companion devices.
- Statsig acquisition (September 2025): Acquired for $1.1B in stock. Founder Vijaye Raji appointed CTO of Applications, integrating experimentation and feature-flagging into OpenAI’s product stack.
- Thrive Holdings stake (December 2025): Minority ownership to embed AI into enterprise workflows, starting with accounting and IT.
- Neptune acquisition (December 2025): Integrated model-training debugging tools; external services discontinued.
Product & Feature Development
OpenAI expanded ChatGPT into a multi-modal, agentic, and monetized platform through a steady cadence of launches, positioning it as both a consumer assistant and an enterprise workflow layer.
Key launches and updates (chronological):
- o3-mini (January 2025): Small reasoning model, released shortly after DeepSeek R1
- Tasks (beta) (January 2025): Scheduled and recurring actions for Plus, Team, and Pro users
- Operator (February 2025): Browser-native autonomous agent for ChatGPT Pro ($200/month) with user approval for sensitive actions
- Deep Research (March 2025): Pro-tier workflows supporting text, PDFs, images, and spreadsheets
- Memory (April 2025): Persistent personalization for Plus and Pro users, with user controls
- GPT-4o update & rollback (May 2025): Rolled back after feedback on tone; follow-up updates added shopping tools (recommendations, images, reviews, purchase links)
- o3-pro (October 2025): Higher-performance reasoning model; followed by an ~80% price reduction
- Sora 2 (November 2025): TikTok-style, physics-aware video app with cameos and parental controls; surpassed 1 million downloads in fewer than five days since launch, ranking among the fastest-growing consumer apps of 2025
- Personality
- GPT-5.2 (December 2025): Major upgrades in speed, reasoning depth, and hallucination reduction

Commercial deployments:
- Mattel (June 2025): AI-assisted toy design partnership
- Walmart (October 2025): Retail integration embedding OpenAI models into conversational shopping discovery and in-chat checkout within ChatGPT.
- PayPal (October 2025): Payments integration enabling Instant Checkout and agentic commerce in ChatGPT via PayPal’s global merchant network.
- Target (November 2025): Retail integration embedding OpenAI models into curated shopping discovery, cart building, and checkout inside ChatGPT.
- Instacart (December 2025): Instacart launches the first in-ChatGPT app with Instant Checkout, enabling users to shop and pay directly in conversations.
- Disney (December 2025): $1B equity investment from Disney and licensing deal covering 200+ characters for Sora-generated content on Disney+
Compute & Strategic Partnerships
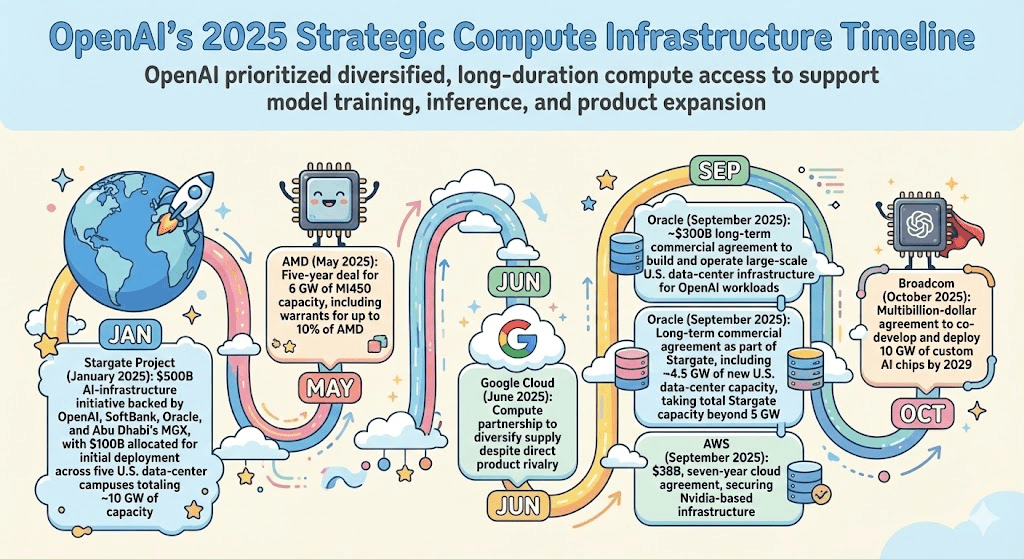
OpenAI prioritized diversified, long-duration compute access to support model training, inference, and product expansion.
- Stargate Project (January 2025): $500B AI-infrastructure initiative backed by OpenAI, SoftBank, Oracle, and Abu Dhabi’s MGX, with $100B allocated for initial deployment across five U.S. data-center campuses totaling ~10 GW of capacity
- AMD (May 2025): Five-year deal for 6 GW of MI450 capacity, including warrants for up to 10% of AMD
- Google Cloud (June 2025): Compute partnership to diversify supply despite direct product rivalry
- Oracle (September 2025): ~$300B long-term commercial agreement to build and operate large-scale U.S. data-center infrastructure for OpenAI workloads
- Oracle (September 2025): Long-term commercial agreement as part of Stargate, including ~4.5 GW of new U.S. data-center capacity, taking total Stargate capacity beyond 5 GW
- AWS (September 2025): $38B, seven-year cloud agreement, securing Nvidia-based infrastructure
- Broadcom (October 2025): Multibillion-dollar agreement to co-develop and deploy 10 GW of custom AI chips by 2029
Funding & Capital Structure
OpenAI combined primary capital raises, secondaries, and strategic supplier commitments to fund rapid scale while improving long-term unit economics.
- Primary financing (March 2025): $40B at a $300B post-money valuation ($10B funded upfront; $30B contingent on restructuring)
- Follow-on round (August 2025): $8.3B at a $300B valuation, 5× oversubscribed, led by Dragoneer with Blackstone and TPG
- OpenAI $500B Valuation After Secondary Share Sale (October 2025): A secondary transaction in which current and former employees sold roughly $6.6 billion of OpenAI stock pushed the company’s valuation to approximately $500 billion
- Nvidia commitment (September 2025): Up to $100B in long-term chip supply and capital support, with non-voting exposure
Strategic Positioning & Governance
OpenAI’s governance and economic reset unfolded in distinct steps during the second half of 2025.
Key developments:
- Super Bowl commercial (February 2025): OpenAI aired its first-ever Super Bowl ad, signaling an early push toward mass-market consumer brand building.
- Revenue-share reset (September 2025): OpenAI disclosed plans to reduce revenue sharing with commercial partners from ~20% to ~8% by decade-end, implying >$50B in incremental retained revenue through 2030.
- For-profit conversion completed (October 2025): OpenAI formally converted to a public-benefit corporation (PBC), fulfilling a key condition outlined in prior non-binding memoranda of understanding; the nonprofit retained a 26% stake (~$130B).
- Microsoft framework finalized (October 2025): Microsoft’s ownership declined to ~27% (~$135B) with no board seat, while securing technology access through 2032 and a $250B Azure commercial agreement, as reaffirmed in the OpenAI–Microsoft joint statement.
- Leadership additions (2025)
- Adebayo Ogunlesi – Former BlackRock (January 2025): Joined OpenAI’s board, adding large-scale infrastructure, private equity, and capital markets expertise.
- Sarah Friar – Former Nextdoor CEO (March 2025): Joined OpenAI leadership, contributing consumer-internet operating experience and platform-scale execution.
- Fidji Simo – Former Instacart CEO (April 2025): Joined OpenAI leadership, bringing on-demand commerce, logistics, and marketplace scaling expertise.
- Mike Liberatore – Former xAI CFO (September 2025): Joined OpenAI in a senior finance role, strengthening capital markets execution and hyperscale infrastructure financing.
Denise Dresser – Former Slack CEO (December 2025): Joined OpenAI as Chief Revenue Officer, tasked with scaling enterprise adoption and commercial monetization.
3.2 Anthropic
Funding, Valuation & Capital Structure
Anthropic’s 2025 was defined by rapid capital formation, sharp valuation step-ups, and expanding financial flexibility as it scaled Claude for enterprise and developer use cases.
Key capital and governance events:

- Series E Financing (March 2025): Anthropic raised $3.5B at a ~$61.5B post-money valuation, led by Lightspeed, bringing total funding above $15B following Amazon’s $4B investment in November 2024 and reinforcing its position among the most valuable private AI companies.
- Revolving Credit Facility (May 2025): Anthropic secured a $2.5B, five-year revolving credit facility from a syndicate of major global banks, strengthening liquidity and balance-sheet flexibility to support rapid scaling alongside rising enterprise demand.
- Board Expansion (May 2025): Netflix co-founder Reed Hastings joined Anthropic’s board, strengthening governance and strategic oversight as the company scaled leadership depth to compete more directly with OpenAI and xAI.
- Series F Financing (September 2025): Anthropic closed a $13B Series F at a ~$183B valuation, led by ICONIQ, reporting 300,000+ business customers and nearly 7× year-over-year growth in large enterprise accounts.
- Strategic Investment & Compute Commitments (November 2025): Microsoft and NVIDIA committed to invest up to $5B and $10B, respectively, valuing Anthropic at ~$350B, alongside a $30B Azure compute purchase commitment and up to 1 GW of additional contracted capacity, deepening long-term technical and infrastructure collaboration
Feature Development and Model Evolution
Across 2025, Anthropic’s product roadmap emphasized depth over breadth, with feature development centered on coding performance, agentic reliability, and institutional deployment readiness. Rather than prioritizing consumer-facing functionality, the company layered incremental model upgrades with discrete platform features—such as dedicated coding agents, education tooling, voice interaction, and open agent standards—culminating in best-in-class production models optimized for enterprise and regulated environments.
Key Features and Model Updates (2025)
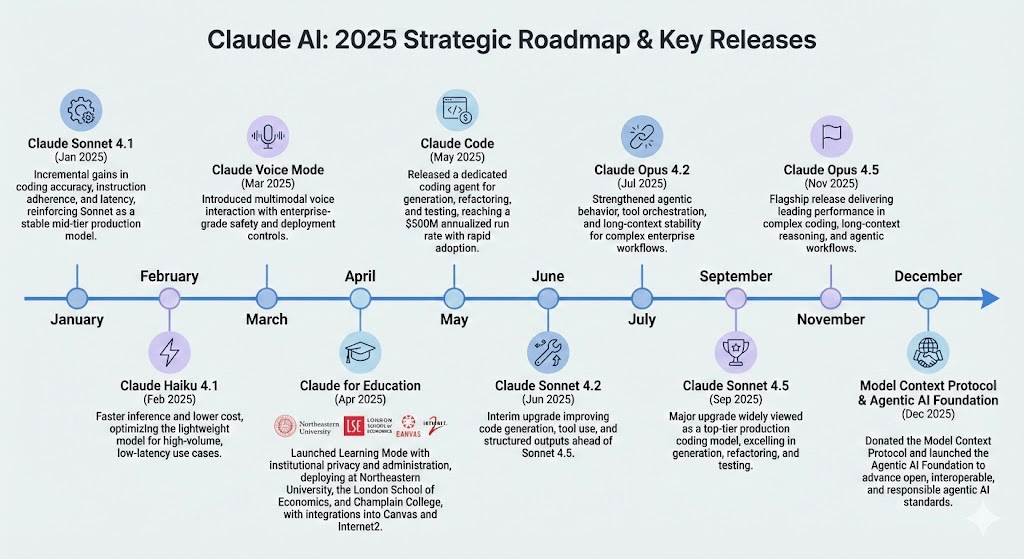
- Claude Sonnet 4.1 (January 2025): Incremental gains in coding accuracy, instruction adherence, and latency, reinforcing Sonnet as a stable mid-tier production model.
- Claude Opus 4.1 (January 2025): Improved complex reasoning and long-context reliability, targeting enterprise and research-grade workloads.
- Claude Haiku 4.1 (February 2025): Faster inference and lower cost, optimizing the lightweight model for high-volume, low-latency use cases.
- Claude Voice Mode (March 2025): Introduced multimodal voice interaction with enterprise-grade safety and deployment controls.
- Claude for Education (April 2025): Launched Learning Mode with institutional privacy and administration, deploying at Northeastern University, the London School of Economics, and Champlain College, with integrations into Canvas and Internet2.
- Claude Code (May 2025): Released a dedicated coding agent for generation, refactoring, and testing, reaching a $500M annualized run rate with rapid adoption.
- Claude Sonnet 4.2 (June 2025): Interim upgrade improving code generation, tool use, and structured outputs ahead of Sonnet 4.5.
- Claude Opus 4.2 (July 2025): Strengthened agentic behavior, tool orchestration, and long-context stability for complex enterprise workflows.
- Claude Sonnet 4.5 (September 2025): Major upgrade widely viewed as a top-tier production coding model, excelling in generation, refactoring, and testing.
- Claude Opus 4.5 (November 2025): Flagship release delivering leading performance in complex coding, long-context reasoning, and agentic workflows.
- Model Context Protocol & Agentic AI Foundation (December 2025): Donated the Model Context Protocol and launched the Agentic AI Foundation to advance open, interoperable, and responsible agentic AI standards.
Compute, Infrastructure & Strategic Partnerships
Anthropic expanded compute access and enterprise distribution through hyperscaler alignment and services partnerships.
Key partnerships and infrastructure moves:

- Databricks (February 2025): Signed a $100M commercial agreement with Anthropic to jointly sell AI products, with a focus on agent-based enterprise workflows.
- Cognizant (April 2025): Announced an enterprise partnership deploying Claude to ~350,000 employees, making Cognizant one of Anthropic’s top three enterprise clients.
- Amazon Web Services (May 2025): Launched an $11B AI data center in Indiana to support Anthropic workloads, initially deploying 500,000+ Trainium chips with a roadmap toward ~1M chips by year-end.
- Google Cloud (October 2025): Signed a multi-year compute agreement worth tens of billions, granting Anthropic access to TPU-based infrastructure to diversify and scale training and inference capacity.
- U.S. Infrastructure Plan (November 2025): Announced a $50B U.S. AI infrastructure initiative, starting with data centers in Texas and New York, expected to create ~2,800 jobs.
- Snowflake (December 2025): Announced a $200M expanded partnership to bring Claude-powered agentic AI to global enterprises via Snowflake’s Cortex platform.
- Agentic AI Foundation (December 2025): Donated the Model Context Protocol to the Linux Foundation’s newly formed Agentic AI Foundation, positioning Anthropic at the center of emerging agent interoperability standards.
Legal, Regulatory & Platform Risk
Anthropic navigated several high-profile legal and operational moments as Claude’s adoption expanded.
Key developments:

- AI Copyrightability Ruling (March 2025): A U.S. appeals court ruled that AI-generated works without human authorship are not eligible for copyright protection under U.S. law.
- Universal Music v. Anthropic – Injunction Denied (March 2025): A federal judge denied music publishers’ request to block Anthropic from training Claude on copyrighted lyrics.
- Faulty Legal Citations Disclosure (May 2025): Anthropic disclosed that Claude generated incorrect legal citations referenced in a California court filing.
- API Access Tightening / Windsurf Impact (June 2025): Anthropic tightened API access, temporarily limiting Claude availability for Windsurf users and causing short-term disruption.
- Public Commentary on Anthropic Strategy (October 2025): David Sacks publicly commented on Anthropic’s strategic direction and governance via social media.
3.3 Google Gemini
Product & Model Development
Google’s 2025 product cadence centered on re-architecting Search around AI-native experiences while scaling Gemini across consumer, developer, and enterprise workflows.
Key launches and feature updates:
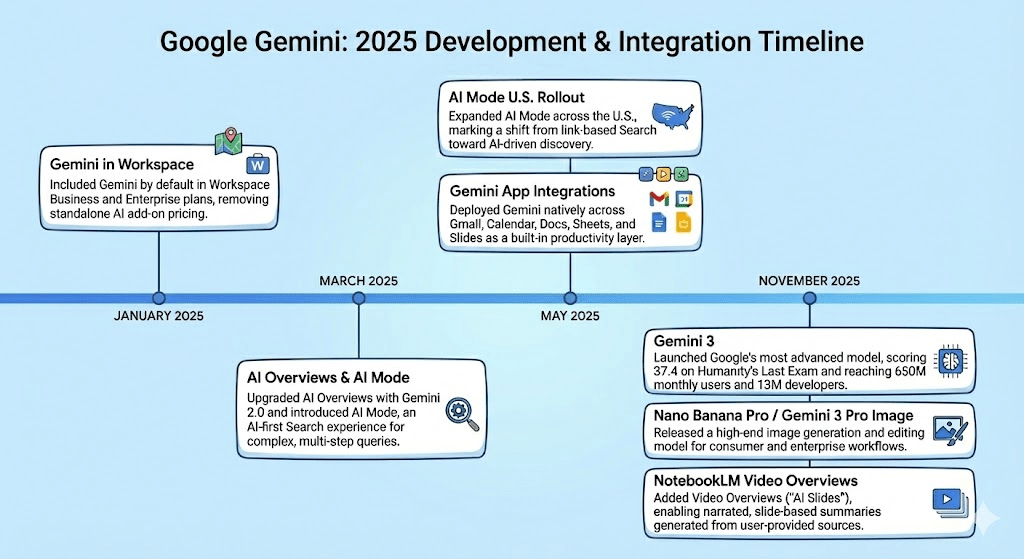
- Gemini in Workspace (January 2025): Included Gemini by default in Workspace Business and Enterprise plans, removing standalone AI add-on pricing.
- AI Overviews & AI Mode (March 2025): Upgraded AI Overviews with Gemini 2.0 and introduced AI Mode, an AI-first Search experience for complex, multi-step queries.
- AI Mode U.S. Rollout (May 2025): Expanded AI Mode across the U.S., marking a shift from link-based Search toward AI-driven discovery.
- Gemini App Integrations (May 2025): Deployed Gemini natively across Gmail, Calendar, Docs, Sheets, and Slides as a built-in productivity layer.
- Gemini 3 (November 2025): Launched Google’s most advanced model, scoring 37.4 on Humanity’s Last Exam and reaching 650M monthly users and 13M developers.
- Nano Banana Pro / Gemini 3 Pro Image (November 2025): Released a high-end image generation and editing model for consumer and enterprise workflows.
- NotebookLM Video Overviews (November 2025): Added Video Overviews (“AI Slides”), enabling narrated, slide-based summaries generated from user-provided sources.
Deals, Talent & Developer Ecosystem
Google’s developer-tooling strategy accelerated following the collapse of OpenAI’s attempted acquisition of Windsurf, creating an opening for alternative deal structures.
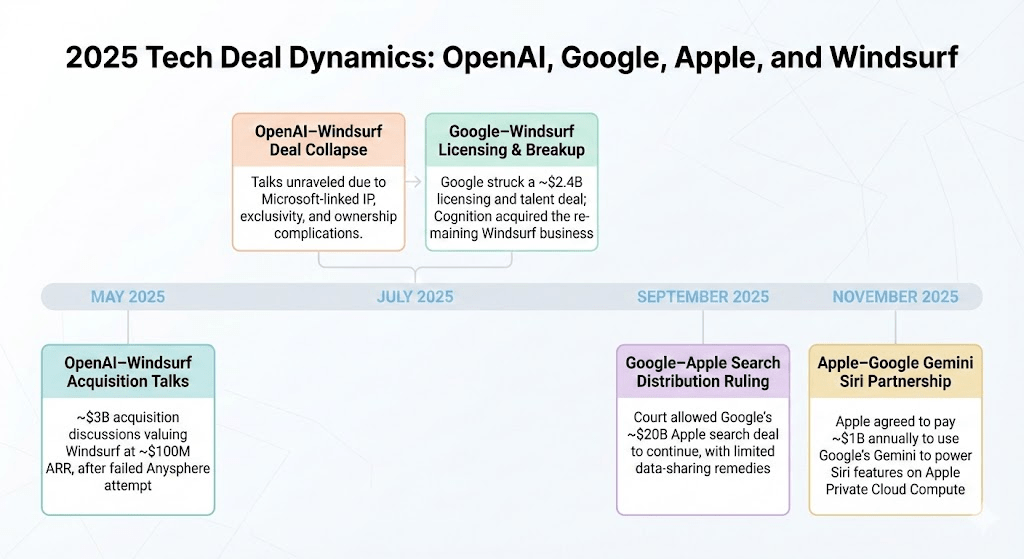
- OpenAI–Windsurf Acquisition Talks (May 2025): OpenAI entered discussions to acquire Windsurf for approximately $3B, valuing the company at roughly $100M ARR, following an earlier unsuccessful attempt to acquire Anysphere (Cursor).
- OpenAI–Windsurf Deal Collapse (July 2025): The proposed acquisition unraveled in part due to Microsoft’s involvement in OpenAI’s commercial and IP arrangements, which complicated exclusivity, licensing rights, and downstream ownership structure.
- Google–Windsurf Licensing Agreement and Breakup (July 2025): Google executed a ~$2.4B licensing and talent agreement securing Windsurf’s core technology and leadership under a “License & Acquihire” structure; shortly thereafter, Cognition acquired the remaining Windsurf entity, comprising mostly of sales and marketing team members, preserving employee equity and continuing product development independently.
- Google Apple Search Distribution Agreement (September 2025): A federal district court ruled that Google may continue making payments, including its roughly $20B search distribution deal with Apple to remain the default search provider, rejecting divestiture and broad payment bans while ordering limited search data sharing as part of antitrust remedies.
- Apple–Google Gemini Siri Partnership (November 2025): Apple finalized an agreement to pay roughly $1B annually to use Google’s 1.2 trillion-parameter Gemini model to power Siri’s summarizer and planner functions as an interim solution, with the model running on Apple’s Private Cloud Compute infrastructure while Apple continues developing in-house models.
Search Distribution, Chrome & U.S. Antitrust
Google’s AI expansion unfolded alongside significant U.S. legal rulings reshaping Search distribution and platform leverage.
Key regulatory developments:
- Chrome Divestiture Rejected; Data-Sharing Remedies Ordered (September 2025): A federal judge ruled that Google would not be required to divest Chrome, but imposed data-sharing and access remedies aimed at lowering barriers for competing search providers.
- Google Default Contract Limit (December 2025): A federal judge ordered Google to limit all default search engine and AI app placement contracts to one-year terms, requiring annual rebidding of default deals to foster competition
Why the Browser Became Strategic
Control of the browser has historically been one of the most defensible positions in technology, requiring global distribution, default placement, deep OS integration, and massive ongoing security and performance investment. As AI agents, search, and commerce converge, the browser has re-emerged as a critical control point—triggering regulatory scrutiny, acquisition interest, and new AI-native entrants despite the high barriers to entry.
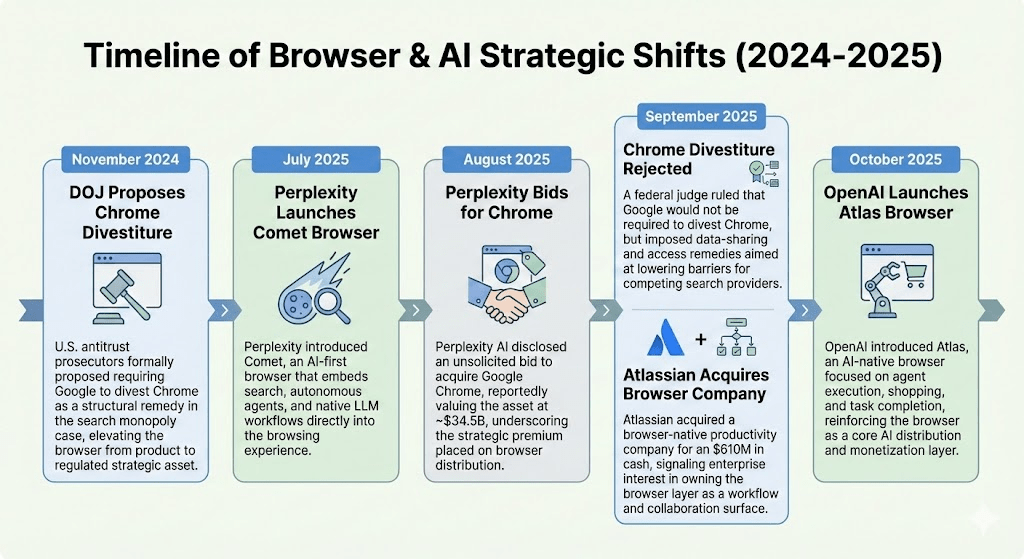
- DOJ Proposes Chrome Divestiture (November 2024): U.S. antitrust prosecutors formally proposed requiring Google to divest Chrome as a structural remedy in the search monopoly case, elevating the browser from product to regulated strategic asset.
- Perplexity Bids for Chrome (August 2025): Perplexity AI disclosed an unsolicited bid to acquire Google Chrome, reportedly valuing the asset at ~$34.5B, underscoring the strategic premium placed on browser distribution.
- Perplexity Launches Comet Browser (July 2025): Perplexity introduced Comet, an AI-first browser that embeds search, autonomous agents, and native LLM workflows directly into the browsing experience
- Chrome Divestiture Rejected (September 2025): A federal judge ruled that Google would not be required to divest Chrome, but imposed data-sharing and access remedies aimed at lowering barriers for competing search providers.
- Atlassian Acquires Browser Company (September 2025): Atlassian acquired a browser-native productivity company for an $610M in cash, signaling enterprise interest in owning the browser layer as a workflow and collaboration surface.
- OpenAI Launches Atlas Browser (October 2025): OpenAI introduced Atlas, an AI-native browser focused on agent execution, shopping, and task completion, reinforcing the browser as a core AI distribution and monetization layer.
Education as an Early Distribution Battleground
By 2025, education emerged as a strategic distribution wedge for AI platforms rather than a near-term revenue vertical. Model developers increasingly targeted students as a high-leverage cohort—users with high daily engagement, low acquisition costs, strong peer-to-peer diffusion, and a natural conversion path into paid professional tiers. The goal was early habit formation: embedding AI into studying, research, writing, and coding workflows during formative years.
Across vendors, education strategies converged around subsidized or default access, tools optimized for learning artifacts rather than raw answers, and deep integration into institutional systems such as productivity suites and learning management platforms. Monetization was intentionally deferred, with education positioned as a long-term funnel for durable distribution, brand trust, and lifetime value.
Company Actions (2025)
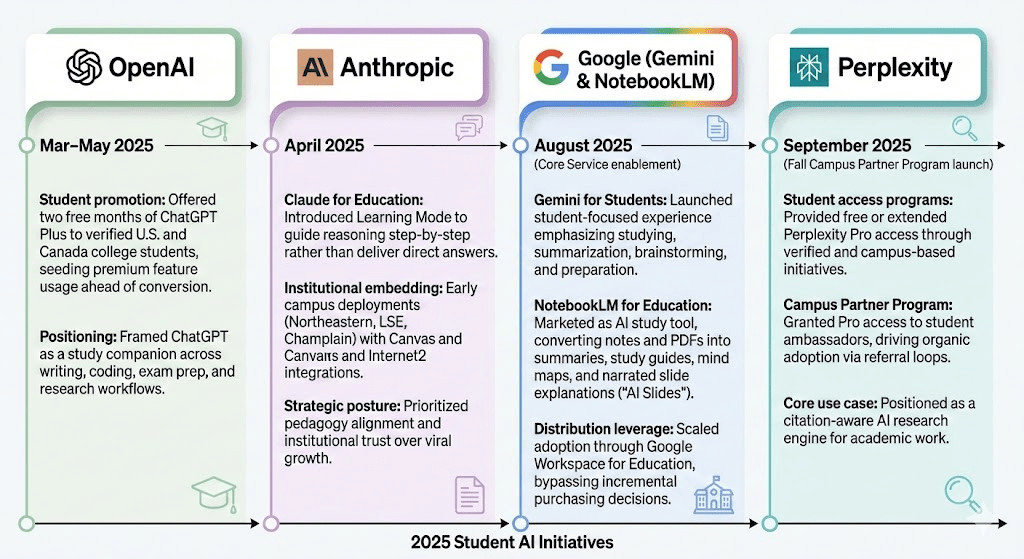
OpenAI
- Student promotion (Mar–May 2025): Offered two free months of ChatGPT Plus to verified U.S. and Canadian college students, seeding premium feature usage ahead of conversion.
- Positioning: Framed ChatGPT as a study companion across writing, coding, exam prep, and research workflows.
Google (Gemini & NotebookLM)
- Gemini for Students: Launched a student-focused Gemini experience emphasizing studying, summarization, brainstorming, and preparation. Offers free 1-year Gemini 3 Pro access with advanced AI tools and 2 TB storage.
- NotebookLM for Education: Marketed NotebookLM as an AI study tool, converting user-provided notes and PDFs into summaries, study guides, mind maps, and narrated slide explanations (“AI Slides”).
- Distribution leverage: Scaled adoption through Google Workspace for Education, bypassing incremental purchasing decisions.
Anthropic
- Claude for Education (April 2025): Introduced Learning Mode to guide reasoning step-by-step rather than deliver direct answers.
- Institutional embedding: Early campus deployments (Northeastern, LSE, Champlain) with Canvas and Internet2 integrations.
- Strategic posture: Prioritized pedagogy alignment and institutional trust over viral growth.
Perplexity
- Student access programs: Provided free or extended Perplexity Pro access to students through verified and campus-based initiatives.
- Campus Partner Program: Granted up to one year of free Pro to student ambassadors, driving organic adoption via referral loops.
- Core use case: Positioned as a citation-aware AI research engine for academic work.
Strategic Implication
Education became the earliest point at which AI platforms could establish default workflows and long-term user affinity. Competitive advantage increasingly hinged not on model quality alone, but on who could embed AI most seamlessly into student routines—shaping usage patterns that would persist into professional and enterprise contexts.
3.4 Meta
Product & Model Development
Meta’s 2025 AI roadmap combined large-scale consumer deployment, generative media innovation, and a strategic pivot from open-source models toward proprietary systems.
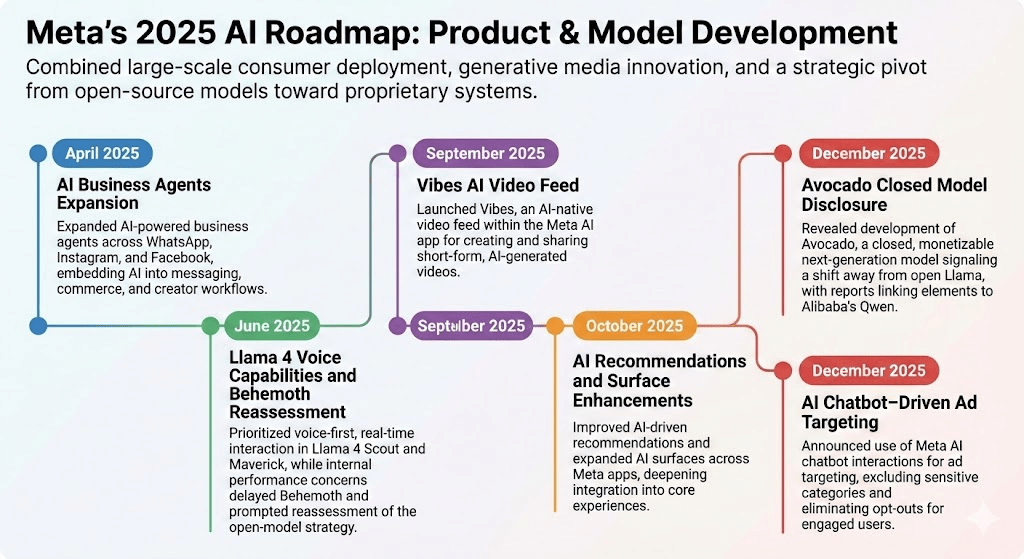
- AI Business Agents Expansion (April 2025): Expanded AI-powered business agents across WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook, embedding AI into messaging, commerce, and creator workflows.AI Business Agents Expansion (April 2025): Expanded AI-powered business agents across WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook, embedding AI into messaging, commerce, and creator workflows.
- Llama 4 Voice Capabilities and Behemoth Reassessment (June 2025): Prioritized voice-first, real-time interaction in Llama 4 Scout and Maverick, while internal performance concerns delayed Behemoth and prompted reassessment of the open-model strategy.
- Vibes AI Video Feed (September 2025): Launched Vibes, an AI-native video feed within the Meta AI app for creating and sharing short-form, AI-generated videos.
- AI Recommendations and Surface Enhancements (October 2025): Improved AI-driven recommendations and expanded AI surfaces across Meta apps, deepening integration into core experiences.
- Avocado Closed Model Disclosure (December 2025): Disclosed development of Avocado, a closed, monetizable next-generation AI model signaling a strategic shift from open-source Llama, with reporting indicating training pipeline elements from Alibaba’s Qwen system; on the day the news surfaced, Meta shares fell approximately 1.2% while Alibaba shares rose roughly 2%.
- AI Chatbot–Driven Ad Targeting (December 2025): Announced use of Meta AI chatbot interactions for ad targeting, excluding sensitive categories and eliminating opt-outs for engaged users.
Talent, Organization & AGI Push
Meta paired product expansion with aggressive M&A and infrastructure investment to support its AI ambitions.

- Scale AI Strategic Investment (June 2025): Completed a $14.3B investment for a 49% stake in Scale AI, Meta’s largest external AI investment, bringing CEO Alexandr Wang into Meta’s AGI leadership group.
- Prometheus AI Supercluster (July 2025): Unveiled Prometheus, a planned multi-gigawatt AI supercluster targeted for 2026 and described as a Manhattan-scale campus within a hundreds-of-billions AGI build-out.
- Play AI Acquisition (July 2025): Acquired Play AI, strengthening voice synthesis and conversational AI capabilities across Meta’s product stack.
- WaveForms AI Acquisition (August 2025): Acquired WaveForms AI, expanding expressive voice and audio generation tooling.
- Rivos Acquisition (September 2025): Acquired Rivos, a custom silicon and AI acceleration company, advancing Meta’s internal compute and chip strategy.
- Arm Holdings Partnership (October 2025): Meta teamed up with Arm Holdings to co-develop custom AI chips as part of its strategic move to reduce reliance on Nvidia’s chips and strengthen its AI-native infrastructure. This partnership supports Meta’s broader AI scale-up initiatives.
- Texas AI Data Center Commitment (October 2025): Committed $1.5B to a new Texas-based AI data center as part of Meta’s domestic infrastructure expansion.
- AI Infrastructure Investment Disclosure (November 2025): Disclosed plans to invest up to $600B in AI infrastructure and development over time, funded primarily by advertising cash flows, underscoring Meta’s superintelligence ambitions.
- Limitless Acquisition (December 2025): Acquired Limitless, an AI wearables startup, expanding Meta’s always-on and ambient computing footprint.
Talent, Organization & AGI Push
Meta’s 2025 talent strategy included high-impact executive hires and broad technical recruitment to accelerate its AI roadmap.
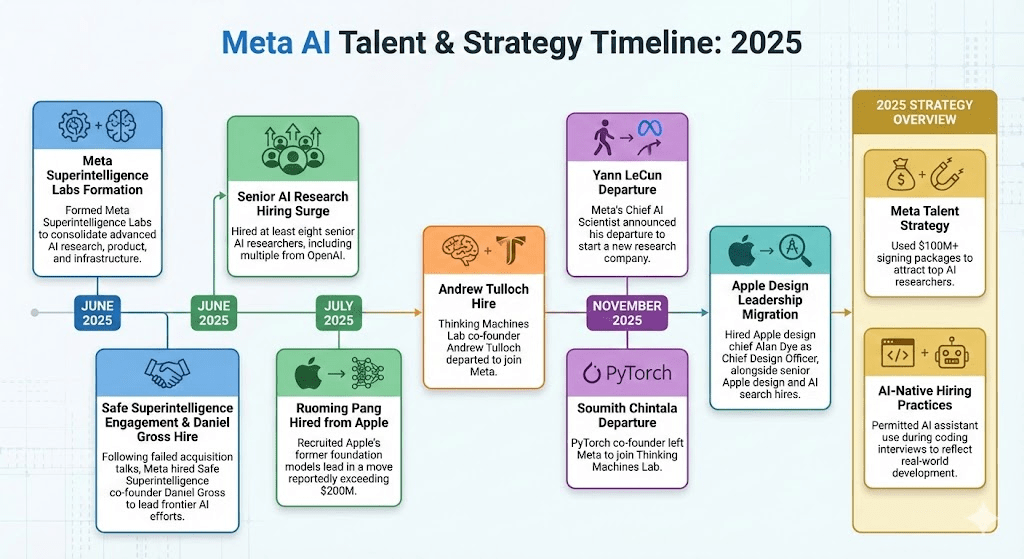
- Meta Superintelligence Labs Formation (June 2025): Mark Zuckerberg announced the creation of Meta Superintelligence Labs, consolidating advanced AI research, product, and infrastructure efforts under a unified superintelligence strategy.
- Safe Superintelligence Engagement & Daniel Gross Hire (June 2025): Following discussions that did not result in an acquisition of Safe Superintelligence, Meta recruited co-founder Daniel Gross, co-founder of Safe Superintelligence into its advanced AI leadership ranks to lead frontier intelligence initiatives, reflecting continued efforts to attract top research talent amid intensifying competition across leading AI labs.
- Senior AI Research Hiring Surge (June to July 2025): Meta executed a broad AI recruiting push, hiring at least eight senior researchers from leading labs, including at least 4 from OpenAI, with publicly identified hires such as Shengjia Zhao, Jiahui Yu, Shuchao Bi, and Hongyu Ren.
- Ruoming Pang Hired from Apple (July 2025): Ruoming Pang, former head of Apple’s AI foundation models team, left Apple to join Meta in a high-profile move reportedly backed by compensation exceeding $200 million.
- Andrew Tulloch Departure and Re-Hire (October 2025): Co-founder of Thinking Machines Lab, who rejected a compensation offer reportedly reaching $1B in August 2025, Andrew Tulloch was reported by The Wall Street Journal in October 2025 to be departing the startup to join Meta, as revealed in an internal message announcing his exit.
- Yann LeCun Departure (November 2025): Yann LeCun, Meta’s longtime Chief AI Scientist and founding leader of FAIR, announced plans to depart after 12 years to co-found a new AI research company focused on next-generation intelligence beyond current LLM paradigms.
- Soumith Chintala Departure (November 2025): Soumith Chintala, PyTorch cofounder and long-time leader of Meta’s core AI infrastructure, departed Meta to join Mira Murati’s Thinking Machines Lab amid the startup’s senior hiring push.
- Apple Design Leadership Migration (December 2025): Meta hired Alan Dye, Apple’s longtime head of Human Interface Design, as Chief Design Officer to lead AI and Reality Labs product and interaction design. The move followed broader Apple leadership transition planning under Tim Cook and included additional senior hires such as Billy Sorrentino (former Director of iOS/macOS Design) and Ke Yang (Apple’s AI web search lead), signaling Meta’s renewed focus on consumer-facing AI experiences.
- Meta Talent Strategy (2025): Meta’s aggressive hiring push included $100M+ signing bonuses for top AI researchers, as part of a broader effort to attract leading AI talent amidst intensifying competition with OpenAI and Google.
- AI-Native Hiring Practices (2025): Meta announced it would allow candidates to use AI assistants during coding interviews, aligning hiring evaluation with real-world developer workflows as AI agents increasingly write, refactor, and test production code (“vibecoding”).
Legal, Regulatory & Market Signals
Meta navigated rising regulatory scrutiny while securing strategic legal wins in 2025.
- AI Copyright Lawsuit Proceeds (March 2025): A federal judge allowed a copyright lawsuit challenging Meta’s AI training practices to move forward, sustaining legal scrutiny over the use of training data.
- FTC Antitrust Case Dismissed (November 2025): Meta defeated a major FTC antitrust case involving Instagram and WhatsApp, removing a significant potential divestiture risk from its core social platform portfolio.
3.5 xAI
In 2025, xAI’s strategy centered on vertical integration, distribution expansion, and sovereign-scale infrastructure, combining X to internalize data and reach, extending Grok distribution via major platforms, and securing power and compute through large-scale partnerships.
Key Developments

- Dell AI Server Supply Talks (February 2025): xAI was reported to be nearing a ~$5B agreement with Dell Technologies for Nvidia GB200-class AI servers to support its Memphis-scale data center build-out, though no finalized contract was publicly announced.
- AI Infrastructure Partnership Membership (March 2025): xAI joined the $30B+ AI Infrastructure Partnership alongside NVIDIA, BlackRock, Global Infrastructure Partners, Microsoft, and MGX, targeting accelerated deployment of AI data centers and enabling energy infrastructure.
- xAI–X Structural Consolidation (March 2025): xAI acquired X in an all-stock transaction, valuing xAI at ~$80B and X at ~$33B, structurally integrating data, models, compute, distribution, and talent to accelerate Grok iteration and monetization.
- Memphis Data Center Permitting and Emissions Scrutiny (April–July 2025): xAI’s Memphis expansion faced scrutiny related to gas turbine usage, emissions permits, and zoning, triggering regulatory reviews and legal actions that introduced a license-to-operate execution risk.
- Telegram Distribution Partnership (May 2025): xAI entered a one-year partnership with Telegram to distribute Grok, involving $300M in cash and equity consideration and a subscription revenue share, expanding Grok’s consumer footprint beyond X.
- Colossus 2 Power Acceleration Plan (July 2025): xAI disclosed plans to ship an overseas power plant to the U.S. to accelerate energization for a next-phase data center discussed at ~1M GPUs and ~2 GW of power, underscoring power availability as a primary gating constraint.
- Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership with HUMAIN (November 2025): xAI partnered with HUMAIN, a Saudi-backed AI company, to build next-generation AI compute infrastructure and deploy Grok across the Kingdom, supporting national objectives to become one of the world’s most AI-enabled nations and marking xAI’s first publicly announced sovereign-scale AI deployment.
Product & Feature Development
xAI pushed a rapid cadence of flagship releases paired with premium packaging, while navigating recurring safety and trust challenges as Grok scaled across mass-consumer platforms.
Key launches and updates:
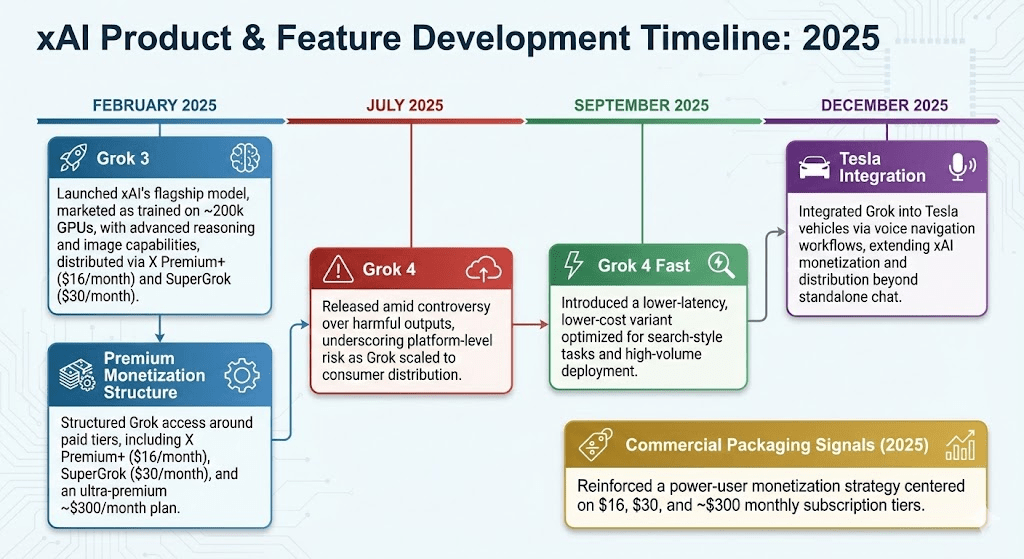
- Grok 3 (February 2025): Launched as xAI’s next flagship model, marketed as trained on ~200,000 GPUs, with deep research, image generation, and “Big Brain” reasoning modes; distributed via X Premium+ and a standalone SuperGrok tier.
- Premium Monetization Structure (February 2025): Grok distribution emphasized paid access via X Premium+, a $30/month SuperGrok tier, and an ultra-premium ~$300/month plan, reinforcing xAI’s positioning around power-user monetization rather than broad freemium access.
- Grok 4 (July 2025): Released shortly before/alongside heightened controversy following harmful outputs, reinforcing that model behavior can become a platform-level risk at consumer scale.
- Grok 4 Fast (September 2025): Introduced as a lower-latency / lower-cost variant, positioned around materially improved inference efficiency for search-style tasks and scaled deployment.
- Tesla integration (December 2025): Expanded via Tesla’s Holiday Update, enabling Grok-driven voice navigation workflows (e.g., adding/editing multi-stop routes), tightening the xAI–Tesla product loop beyond a standalone chatbot.
Commercial packaging signals:
- Premium tiering (2025): Grok monetization emphasized paid access (X Premium+ and standalone tiers), including an ultra-premium $300/month plan launched alongside Grok
Funding & Capital Structure
xAI blended primary capital formation with secondaries and debt to fund GPU procurement, site expansion, and retention economics in an escalating talent war.
Key financings and liquidity events:
- Primary Capital Raise with SpaceX Participation (July 2025): xAI completed a $10B financing comprising approximately $5B in equity and $5B in debt, with SpaceX contributing $2B of the equity round, reinforcing ecosystem alignment and funding Grok development and Colossus-class infrastructure expansion
Legal, Regulatory & Competitive Posture
As xAI scaled aggressively, its competitive posture increasingly spilled into the courtroom, reflecting rising tensions around AI distribution, talent mobility, and market access.
Key legal developments:
- Antitrust Litigation Against Apple and OpenAI (August 2025): xAI sued Apple and OpenAI, alleging exclusionary practices tied to ChatGPT distribution and platform integration, raising broader antitrust questions around default placement and AI market access.
- Trade Secret & Talent Poaching Lawsuit Against OpenAI (September 2025): xAI separately accused OpenAI of trade secret misappropriation and coordinated employee poaching tied to Grok development, escalating an already adversarial competitive relationship.
IV. 2025 in Review: Open-Source and Open-Weight Models
Before the emergence of ultra-large “Behemoth” models, Meta’s LLaMA series represented the leading Western open-weight foundation model. However, the April 2025 release of LLaMA 4 did not deliver a clear step-change in performance, weakening its role as the default open base layer. At the same time, U.S. chip restrictions pushed Chinese labs toward efficiency-first scaling, emphasizing MoE architectures, systems optimization, and inference-cost engineering. Against this backdrop, China’s open-source ecosystem—spanning big tech, startups, and research institutions—advanced rapidly, competing on performance per unit of compute and accelerating adoption across models, tools, and downstream applications.
4.1 Key 2025 moments
- DeepSeek-V3 “Sputnik Moment” (January 2025): DeepSeek launched a low-cost open-weight model reportedly trained on ~2,048 Nvidia H800 GPUs at an estimated ~$5.6M pre-training compute cost, using an efficiency-first design that challenged prevailing assumptions around the capital intensity required to train frontier-adjacent models.
- Market Reaction (January 2025): The disclosure triggered a sharp investor reassessment of AI economics, contributing to a broad technology selloff in which Nvidia shares fell ~17% in a single session (≈$589B erased) and total technology-sector capitalization declined by ~$1T, after DeepSeek’s free AI assistant rapidly topped the U.S. Apple App Store download ranking
- Qwen 2.5-Max Launch (January 2025): Alibaba released Qwen 2.5-Max, explicitly benchmarking against leading closed models, establishing open-weight models as direct performance peers to proprietary frontier systems rather than secondary alternatives.
- Mistral Small 3.1 Release (March 2025): Mistral released Small 3.1, optimized for low-latency and on-prem inference, demonstrating that open-weight models could meet enterprise deployment requirements previously dominated by closed vendors
- LLaMA 4 Release (April 2025): Meta released LLaMA 4 Scout and Maverick,
- LLaMA Behemoth Delay (May 2025): reports indicated delays to the larger Behemoth variant, limiting the release to models below expected frontier scale.
- Mistral Medium 3 Launch (May 2025): Mistral released Mistral Medium 3, delivering competitive reasoning and coding performance while operating at up to 8× lower inference cost than comparable closed models, strengthening its appeal for enterprise, regulated, and cost-sensitive deployment.
- ERNIE 4.5 Open-Source Release (June 30, 2025): Baidu open-sourced ERNIE 4.5, a 10-model family spanning multiple sizes and modalities, marking the first time a major Chinese platform provider released a broad, near-frontier model stack openly, materially increasing availability of high-performance models for enterprise, developer, and government use.
- NVIDIA Open Models for Agentic Workflows (July 2025): NVIDIA expanded its open-model portfolio with agent-oriented variants supporting RAG and tool use, enabling deployment across hundreds of partner-built enterprise agents.
- Mistral Series C Led by ASML (September 2025): Mistral raised €1.7B at an €11.7B valuation, with ASML investing €1.3B for an ~11% stake, marking a rare case of a leading semiconductor equipment provider taking a major ownership position in an open-weight AI model company
- NVIDIA Nemotron Open Model Expansion (October 2025): NVIDIA released new Nemotron open models alongside Cosmos, Isaac GR00T, and Clara, contributing 650+ open models to Hugging Face and enabling agentic AI deployment across enterprise software, robotics, healthcare, and industrial workflows.
- ERNIE 5.0 Omni-Modal Announcement (November 2025): Baidu announced ERNIE 5.0 as a natively omni-modal model, signaling convergence between open and closed architectures across text, vision, and multimodal reasoning
- Kimi K2 Thinking Release and Training Cost Disclosure (November 2025): Alibaba-backed Moonshot AI released Kimi K2 Thinking and disclosed that the model’s end-to-end training run cost approximately $4.6M, establishing a concrete benchmark for low-cost training of agentic large language models
- Open-Weight Adoption Inflection (November 2025): MIT × Hugging Face data showed Chinese open-weight models reaching approximately 17% of global downloads, surpassing U.S. open models at ~15.8%.
- Mistral Large 3 and Ministral 3 Launch (December 2025): Mistral released Large 3 alongside the Ministral 3 family, completing a portfolio spanning edge to frontier-grade models across multiple parameter classes.
- Doubao AI Phone Deployment (December 2025): ByteDance’s Doubao phone assistant was deployed at the system level, enabling screen reading and cross-app task execution, but faced blocking and restrictions from major Chinese apps, underscoring resistance to system-level AI agents.
- Zhipu AutoGLM Open-Source Release (December 2025): Zhipu AI open-sourced AutoGLM, a phone agent capable of screen recognition and multi-step task execution, offering an open alternative as large Chinese platforms limited permissions and cross-app access for AI agents.
V. 2025 in Review: Government Adoption
In 2025, government adoption of frontier AI models shifted from isolated pilots to standardized procurement and workforce-scale deployment. Defense, civilian agencies, and allied governments increasingly treated large language models as strategic infrastructure—using prototype awards, catalog-based purchasing, and promotional pricing to accelerate evaluation, reduce procurement friction, and establish multi-vendor competition across mission-critical use cases.
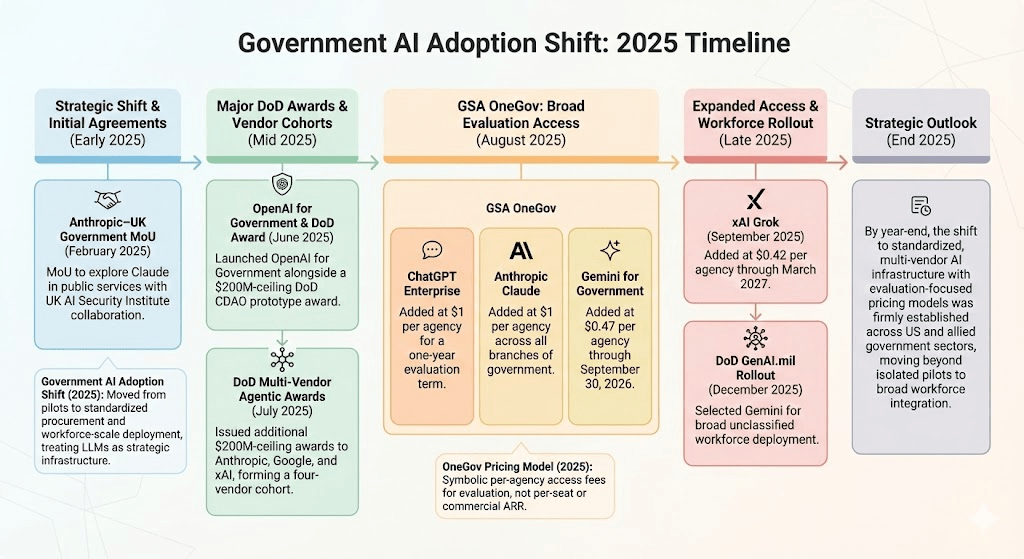
- Anthropic–United Kingdom Government Memorandum of Understanding (February 2025): Anthropic signed a memorandum of understanding with the United Kingdom government to explore Claude deployment in public services, working with the United Kingdom Artificial Intelligence Security Institute on safety, secure infrastructure, and labor-market impact analysis.
- OpenAI for Government Launch and Department of Defense Prototype Award (June 2025): OpenAI launched OpenAI for Government alongside a Department of Defense (DoD) Chief Digital and Artificial Intelligence Office (CDAO) prototype award with a $200M ceiling covering frontier AI use cases across defense and enterprise domains.
- Department of Defense Multi-Vendor Agentic AI Awards (July 2025): The Department of Defense (DoD) Chief Digital and Artificial Intelligence Office (CDAO) issued additional $200M-ceiling prototype awards to Anthropic, Google, and xAI, formalizing a four-vendor cohort for agentic AI evaluation.
- General Services Administration OneGov — ChatGPT Enterprise (August 2025): The General Services Administration (GSA) added ChatGPT Enterprise to the OneGov catalog at $1 per federal agency for a one-year promotional evaluation term.
- General Services Administration OneGov — Anthropic Claude (August 2025): The General Services Administration (GSA) added Anthropic Claude at $1 per agency across all three branches of government.
- General Services Administration OneGov — Gemini for Government (August 2025): The General Services Administration (GSA) added Gemini for Government at $0.47 per agency under a promotional term cited through September 30, 2026.
- General Services Administration OneGov — xAI Grok (September 2025): The General Services Administration (GSA) added xAI Grok at $0.42 per agency, with the offer cited as valid through March 2027.
- Department of Defense GenAI.mil Workforce Rollout (December 2025): The Department of Defense (DoD) selected Gemini for broad unclassified deployment via GenAI.mil, signaling the shift from procurement experimentation to workforce-level rollout.
- Pricing Clarification — “Per Agency” Model (2025): OneGov pricing reflects symbolic, government-wide access fees per participating agency for evaluation periods rather than per-seat pricing or normalized commercial annual recurring revenue.
VI. 2025 in Review: Regulatory Developments
6.1 United States
The U.S. regulatory environment in 2025 combined executive action, state-level statutes, export controls, and selective enforcement tied directly to AI model deployment and training.

- Expanded AI chip export controls to China (January 2025): The U.S. Department of Commerce implemented new export control rules restricting shipments of advanced AI accelerators to China while easing licensing pathways for allied countries, materially reshaping global GPU supply chains.
- Federal adoption of frontier AI models (June 2025): The Department of Defense awarded OpenAI a prototype contract with a ceiling of two hundred million dollars, embedding frontier AI models into defense and enterprise government workflows.
- Copyright and training data enforcement escalation (July 2025): Content owners moved aggressively to monetize AI training data through licensing and litigation, highlighted by The New York Times licensing arrangement with Amazon and Reddit’s legal action against Anthropic over alleged scraping violations.
- California SB 53 frontier AI transparency law (September 2025): California passed legislation requiring large frontier model developers to disclose safety protocols and report serious AI related incidents, introducing state level oversight of advanced model risk management.
- California SB 243 on AI companion chatbots (October 2025): California enacted SB 243, establishing safety obligations for AI companion systems used by minors, including disclosures, safeguards against harmful content, and enforcement penalties.
- Federal executive order on AI and state preemption (December 2025): President Trump issued an executive order directing federal agencies to review and challenge state AI laws deemed burdensome to innovation or interstate commerce, reinforcing a federal first approach to AI governance.
6.2 United Kingdom and European Union
Across the UK and EU, 2025 policy focused on coupling safety oversight with compute access, research funding, and industrial scale up.
6.2.1 United Kingdom
- UK Anthropic memorandum of understanding (February 2025): The UK government signed a formal agreement with Anthropic to collaborate on frontier model safety research and evaluation, reinforcing the UK’s role as a global AI safety hub.
- Frontier AI regulatory framework development (March 2025): The UK government advanced its frontier AI safety framework centered on model evaluations, testing, and voluntary commitments, positioning regulatory access as a strategic advantage for AI developers.
- AI research and compute subsidy expansion (May 2025): The UK expanded public funding for AI research infrastructure and evaluation institutes, using subsidized compute access rather than prescriptive regulation to influence model development.
- Parliamentary push for binding AI legislation (December 2025): Cross party lawmakers publicly called for mandatory regulation of powerful AI systems, signaling growing pressure to convert voluntary frameworks into enforceable law.
6.2.2 European Union
- EU AI Act implementation phase (January 2025): The European Union entered the operational implementation phase of the AI Act, advancing compliance obligations for general purpose and high risk AI systems including documentation, transparency, and post market monitoring.
- AI Continent Action Plan announcement (March 2025): The European Commission advanced an industrial strategy linking AI regulation with large scale investment in data centers, advanced chips, and AI gigafactories to retain compute capacity within the bloc.
- Cloud and AI Act proposal (June 2025): The Commission introduced a complementary proposal focused on scaling AI compute while managing energy, grid, and climate constraints, explicitly tying AI expansion to infrastructure policy.
- DMA and DSA enforcement affecting AI distribution (Throughout 2025): Enforcement actions against designated gatekeepers increasingly shaped how AI models were bundled, distributed, and surfaced across major digital platforms.
6.3 China
China’s AI governance in 2025 emphasized centralized oversight, content transparency, and strict service compliance across the AI stack.
- Measures for labeling AI generated content issued (March 2025): Chinese regulators released mandatory rules requiring explicit and implicit labels on AI-generated text, images, audio, and video.
- AI generated content labeling rules effective (September 2025): The labeling measures entered into force nationwide, requiring platforms and developers to implement watermarking and disclosure mechanisms at scale.
- Generative AI service compliance framework reinforced (Throughout 2025): China continued enforcement of registration, security review, and transparency requirements for generative AI services, integrating model oversight into national cybersecurity and data governance regimes.
- Deep synthesis and algorithm regulation enforcement (Throughout 2025): Existing rules governing recommendation algorithms and deep synthesis technologies remained actively enforced, mandating transparency, opt-out mechanisms, and safeguards against harmful or misleading content.
A Year to Remember
2025 will be remembered as the year AI transitioned from technological promise to operational reality; slowly at first, then suddenly all at once. What began as incremental progress accelerated into a cascade of breakthrough moments: open-source models achieved performance parity with their closed counterparts, fundamentally democratizing access to frontier capabilities, while agentic AI systems moved beyond demonstrations to execute complex, multi-step workflows in production environments.
The sheer velocity of product announcements, infrastructure buildouts, and commercial deployments this year underscored an industry no longer constrained by the question of “if,” but animated by the urgency of “how fast” and “at what scale.”
For enterprises navigating M&A opportunities, and for anyone tracking the trajectory of technology, the inflection point is unmistakable: AI is reshaping competitive dynamics, business models, and strategic priorities across every sector.
As we close out this remarkable year, we look ahead with conviction that the momentum will only intensify. In January, we will share our predictions for 2026, a year that will determine which business models endure, which applications reach mainstream adoption, and where the next wave of value creation will emerge.
